How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill increasingly sought after, whether for recreational purposes, professional filmmaking, or even surveying. This guide delves into the intricacies of drone operation, from understanding the fundamental components to mastering advanced maneuvers and aerial photography techniques. We’ll cover everything from pre-flight checklists and safety protocols to troubleshooting common issues, ensuring you’re well-equipped to take to the skies with confidence.
Understanding your drone’s mechanics is crucial for safe and successful operation. This guide provides a clear, step-by-step approach, empowering both novice and experienced pilots to enhance their skills and unlock the full potential of their drone. We will explore various flight modes, camera controls, and essential safety measures, equipping you with the knowledge to navigate different environments and capture stunning aerial footage.
Drone Parts and Components
Understanding the individual components of your drone is crucial for safe and efficient operation. This section details the major parts, their functions, and potential points of failure. A solid grasp of these elements allows for better troubleshooting and maintenance.
Drone Component Breakdown

| Component | Function | Potential Failure Points |
|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Generate thrust for lift and maneuverability. | Cracks, bends, imbalance, wear and tear. |
| Motors | Rotate the propellers, providing the necessary power. | Burnout, overheating, malfunctioning ESC (Electronic Speed Controller). |
| Flight Controller | The “brain” of the drone; processes sensor data and controls motor speeds for stable flight. | Software glitches, sensor malfunctions (gyroscope, accelerometer, barometer), physical damage. |
| Battery | Provides power to all drone components. | Over-discharge, cell imbalance, physical damage, age-related degradation. |
| GPS Module | Provides location data for autonomous flight and features like Return-to-Home (RTH). | Signal loss (due to obstructions or weak signal), malfunction. |
| Camera | Captures images and videos. | Lens damage, sensor malfunction, gimbal issues. |
| Gimbal | Stabilizes the camera, ensuring smooth footage. | Motor failure, mechanical wear, software issues. |
| Radio Transmitter (Remote Controller) | Sends control signals to the drone. | Battery depletion, signal interference, physical damage. |
Drone Battery Types and Characteristics
Different drone batteries offer varying performance characteristics. Choosing the right battery is vital for flight time and overall performance.
| Battery Type | Energy Density (Wh/kg) | Typical Flight Time | Charging Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| LiPo (Lithium Polymer) | 150-250 | 15-30 minutes (varies greatly by drone and usage) | Specialized LiPo charger, typically requires balance charging. |
| LiHV (Lithium Polymer High Voltage) | Higher than LiPo | Slightly longer than LiPo | Specialized LiPo charger capable of handling higher voltages. |
| LiFe (Lithium Iron Phosphate) | Lower than LiPo | Shorter than LiPo | Simpler charging process, less prone to damage from overcharging. |
Note: These are general ranges; specific values depend on battery capacity and drone model.
Flight Controller Functionality
The flight controller is the central processing unit of the drone, integrating data from various sensors (accelerometer, gyroscope, barometer, GPS) to maintain stability and execute commands from the remote. It communicates with the motors via Electronic Speed Controllers (ESCs) to adjust their speed and direction, enabling precise flight control.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist and adherence to safety procedures are paramount for preventing accidents and ensuring a safe flight. This section Artikels essential steps and guidelines.
Pre-Flight Checklist
- Check battery level (ensure sufficient charge for the planned flight duration).
- Inspect propellers for damage (cracks, bends).
- Verify GPS signal strength (ensure a strong signal before takeoff).
- Assess the surrounding environment (identify potential obstacles, wind conditions, and airspace restrictions).
- Check the drone’s overall condition (ensure no visible damage or loose parts).
- Confirm radio controller connection and battery level.
- Review flight plan and intended area of operation.
Safety Procedures
Before flight: Always check local regulations and airspace restrictions. Ensure you have the necessary permissions and licenses. Inform others of your flight plan.
During flight: Maintain visual line of sight with the drone at all times. Avoid flying near people, buildings, or other obstacles. Be mindful of wind conditions and adjust flight accordingly.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating this process requires learning about airspace regulations and practicing safe flight maneuvers. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, including practical tips and safety protocols, you can consult this excellent resource on how to operate a drone to enhance your skills and knowledge.
Ultimately, proficient drone operation hinges on consistent practice and a thorough understanding of the technology.
After flight: Land the drone in a safe and designated area. Power off the drone and securely store it and its components. Review footage and ensure compliance with regulations.
Safe Flight Zone Representation
Visualize a safe flight zone as a circle around the pilot. The inner circle represents the immediate area (a few meters radius) requiring extra caution due to potential for uncontrolled impacts. The outer circle extends to the maximum safe range, considering wind conditions, obstacles (trees, buildings, power lines), and airspace restrictions. Factors like wind direction and strength significantly affect the safe flight zone, requiring adjustments to maintain safety.
Basic Drone Operation and Controls
This section covers the fundamentals of operating a drone, including understanding controls, taking off, and landing.
Drone Remote Control Mapping
| Control Stick/Button | Action |
|---|---|
| Left Stick (Vertical) | Throttle (up/down movement) |
| Left Stick (Horizontal) | Yaw (rotation left/right) |
| Right Stick (Vertical) | Pitch (forward/backward movement) |
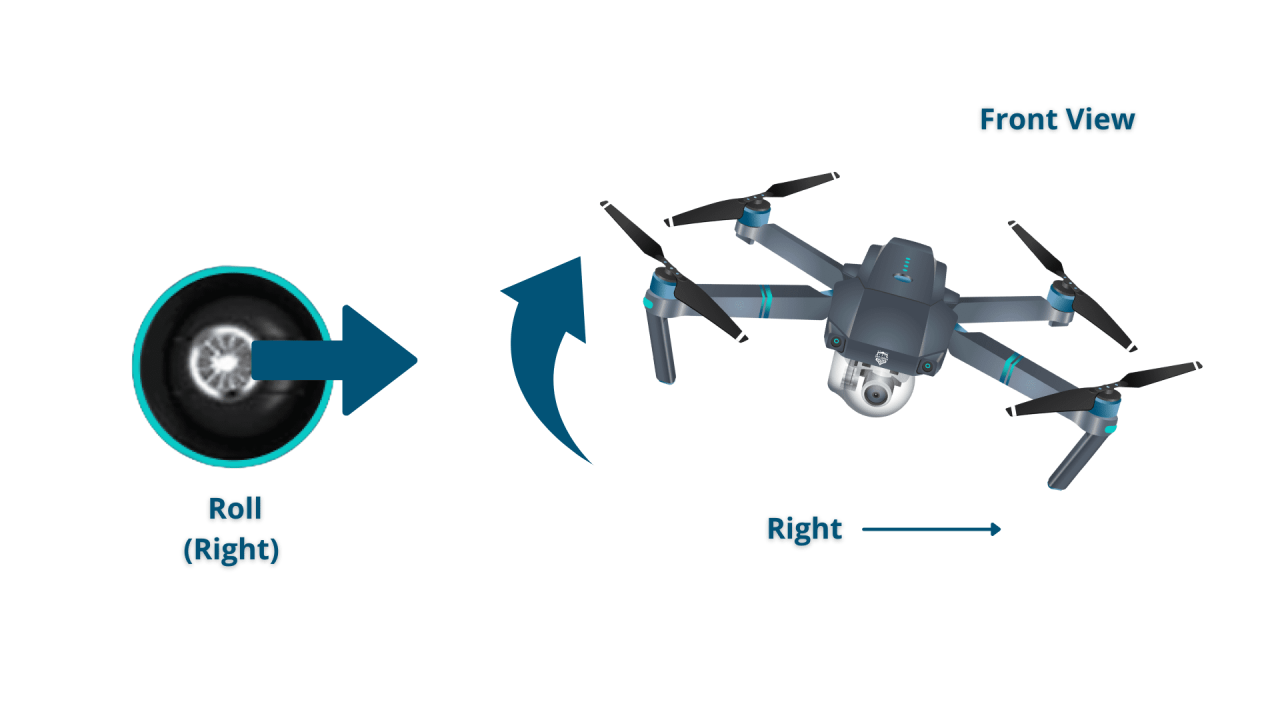
| Right Stick (Horizontal) | Roll (left/right movement) |
| Other Buttons | Camera control (photo/video recording, zoom), Return-to-Home (RTH), flight mode selection. |
Step-by-Step Drone Operation
- Power on the remote controller and drone.
- Wait for the GPS signal to lock (indicated by lights or beeps).
- Calibrate the drone’s compass (if necessary, as per manufacturer’s instructions).
- Gently increase the throttle to lift off.
- Hover at a safe height.
- Use the control sticks to move the drone forward, backward, left, and right.
- To land, gently lower the throttle until the drone touches down.
- Power off the drone and remote controller.
Flight Modes
Most drones offer different flight modes to cater to various skill levels and situations. Beginner mode often limits speed and responsiveness, enhancing stability. Expert mode provides full control, allowing for more advanced maneuvers. GPS mode uses GPS data for position holding and autonomous features like Return-to-Home (RTH).
Advanced Drone Maneuvers and Techniques
This section explores advanced piloting skills, including precise maneuvers and techniques for challenging environments.
Advanced Maneuvers
Precise hovering requires subtle adjustments to the control sticks, maintaining a steady position without drifting. Quick turns involve rapid, controlled movements of the yaw stick. Smooth transitions between movements necessitate coordinated control of all sticks to avoid jerky or abrupt changes in direction.
Challenging Environments
Windy conditions demand careful adjustments to maintain stability. Use the throttle to counteract wind gusts, and be prepared to land if conditions become unsafe. Navigating areas with obstacles requires careful planning and precise control, maintaining a safe distance from any potential hazards.
Cinematic Filming Techniques
Smooth cinematic shots are achieved through coordinated control of the drone’s movement and camera functions. Use the pan, tilt, and zoom controls to frame shots effectively, adjusting speed and direction for dynamic visuals. Smooth, controlled movements are key to avoiding shaky footage.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Issues
This section provides guidance on identifying and resolving common drone problems.
Common Drone Problems
- Low battery
- GPS signal loss
- Motor failure
- Gimbal malfunction
- Radio interference
- Propeller damage
- Flight controller error
Troubleshooting Steps, How to operate a drone
Troubleshooting steps vary depending on the specific problem. For low battery, recharge the battery. For GPS signal loss, move to an area with a clear sky and strong signal. Motor failure may require replacing the motor or ESC. Gimbal malfunction could indicate a mechanical or software issue, requiring calibration or repair.
Radio interference necessitates finding a less congested frequency. Propeller damage requires replacing damaged propellers. Flight controller errors often require firmware updates or a reset.
Troubleshooting Decision Tree (Text-Based)
Drone won’t power on: Check battery and connections. Drone powers on but won’t lift off: Check battery level, GPS signal, and propellers. Drone is unstable in flight: Check wind conditions and calibrate sensors. Drone loses signal: Check radio controller battery and surroundings for interference. Drone crashes: Inspect for physical damage to the drone and propellers.
Drone Photography and Videography
This section provides guidance on capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos.
Drone Camera Settings
| Setting | Effect on Image Quality |
|---|---|
| Aperture | Controls depth of field; wider apertures (lower f-numbers) create shallower depth of field, blurring backgrounds. |
| Shutter Speed | Controls motion blur; faster shutter speeds freeze motion, while slower speeds create motion blur. |
| ISO | Controls sensitivity to light; higher ISO values increase sensitivity, but can introduce noise (grain). |
Capturing High-Quality Footage
Good composition is key, employing the rule of thirds and leading lines. Optimal lighting avoids harsh shadows and overexposure. Stabilization techniques (using a gimbal and smooth movements) minimize shakiness.
Editing Drone Footage

Software options include Adobe Premiere Pro, DaVinci Resolve, and Final Cut Pro. Common editing techniques include color grading, stabilization, and adding music/sound effects.
Mastering the art of drone operation is a journey of continuous learning and practice. By understanding the fundamental components, adhering to safety procedures, and honing your piloting skills, you can unlock a world of possibilities. From breathtaking aerial photography to efficient data collection, the skills acquired here will serve as a solid foundation for your drone adventures. Remember, responsible and safe operation is paramount, ensuring both your safety and the safety of others.
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. A crucial aspect is learning the controls themselves, and a helpful resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques. Successfully operating a drone requires consistent practice and a thorough understanding of safety protocols.
So, take to the skies, explore new heights, and capture stunning perspectives!
FAQ Resource: How To Operate A Drone
What is the legal framework surrounding drone operation?
Drone laws vary by country and region. It’s crucial to research and understand the specific regulations in your area regarding registration, airspace restrictions, and permitted flight zones before operating a drone.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Regular compass calibration is recommended, especially after significant travel or if you experience unusual flight behavior. Consult your drone’s manual for specific instructions.
What should I do if my drone loses GPS signal?
If your drone loses GPS signal, immediately switch to a lower flight mode (if available), and attempt to bring it down slowly and carefully. Avoid abrupt maneuvers.
How can I improve the battery life of my drone?
Store your batteries in a cool, dry place, avoid fully charging or discharging them consistently, and use appropriate charging equipment.
