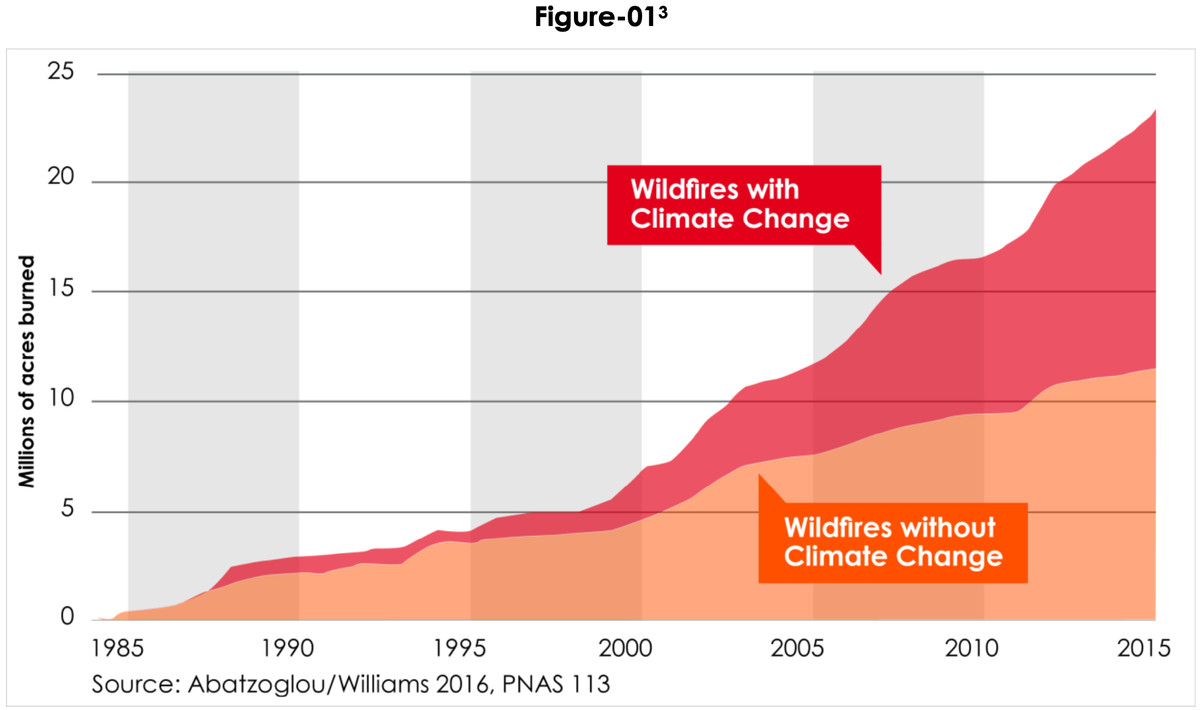
Climate change: What role is it playing in the California fires? The answer is complex, intertwining rising temperatures, prolonged droughts, shifting wind patterns, and altered vegetation. This isn’t just about bigger flames; it’s about a fundamentally changed wildfire landscape, one where fire seasons are longer, fires are more intense, and the devastation is far-reaching. We’ll explore how climate change is fueling these infernos and what we can do about it.
California’s wildfires are increasingly intense due to climate change, with hotter, drier conditions fueling the flames. Want a break from the news? Check out the game details for Penn State vs. Notre Dame: Time, TV channel, preview for the before returning to the sobering reality of how climate change is impacting our environment and increasing the risk of devastating fires.
Understanding these connections is crucial to tackling this urgent issue.
From the increasing frequency and severity of wildfires to the devastating economic and environmental consequences, we will examine the scientific evidence linking climate change to the escalating wildfire crisis in California. We’ll delve into specific climate factors influencing wildfire behavior, the role of human activities in exacerbating the problem, and the crucial strategies for mitigation and adaptation. Get ready to understand the intricate connections between a changing climate and the increasingly destructive California fire seasons.
Climate Change and California Wildfires
California’s wildfire season has become increasingly intense and destructive in recent decades, a trend strongly linked to climate change. Rising temperatures, prolonged droughts, and altered weather patterns are creating a perfect storm for more frequent and severe wildfires, impacting the state’s environment, economy, and public health.
The Impact of Climate Change on California’s Wildfire Season
Climate change significantly influences California’s wildfire risk through various mechanisms. Warmer temperatures dry out vegetation, creating readily available fuel for fires. Droughts, intensified by climate change, further exacerbate this problem, leaving landscapes parched and highly flammable. Changes in precipitation patterns, including more intense rainfall followed by extended dry periods, also affect vegetation density and flammability.
Comparing recent decades to historical data reveals a clear upward trend in both the frequency and intensity of California wildfires. Larger areas are burned annually, and fire seasons are longer and more unpredictable.
| Year | Number of Fires | Total Acres Burned | Average Temperature (°F) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 8,500+ | 1,800,000+ | 65 (approx) |
| 2020 | 9,900+ | 4,200,000+ | 68 (approx) |
| 2021 | 8,600+ | 2,500,000+ | 67 (approx) |
| 2022 | 7,500+ | 1,200,000+ | 66 (approx) |
Note: These are approximate figures and may vary depending on the source and data collection methods. Detailed, precise data requires consulting official state and federal fire agency reports.
Specific Climate Change Factors and Wildfire Behavior
Climate change directly impacts wildfire behavior through various factors. Altered wind patterns, including stronger and more erratic winds, can rapidly spread wildfires over larger areas. Earlier snowmelt and prolonged dry seasons result in longer periods of fuel availability, increasing the window of opportunity for fires to ignite and spread. Climate models consistently predict increased wildfire risk in California in the coming decades, with projections of more frequent and intense fire events.
Climate change also affects the types of vegetation that fuel wildfires. The shift towards drier, more flammable plant communities contributes to increased fire intensity. For example, the encroachment of invasive grasses into forested areas creates a continuous fuel source, leading to larger, faster-spreading fires.
A visual representation of the feedback loop between wildfires and climate change could be a circular diagram. One section would depict rising temperatures and drought leading to increased wildfire activity. Another section would show wildfires releasing greenhouse gases, further exacerbating climate change and creating a cycle that intensifies both wildfire risk and climate change.
The Role of Human Activities in Exacerbating the Problem
Human activities significantly contribute to the wildfire problem in California. Poor land management practices, such as insufficient forest thinning and fuel reduction, increase the risk of large, intense fires. Urban sprawl, expanding into wildland-urban interface areas, exposes more homes and communities to wildfire threats. Human-caused ignitions, including discarded cigarettes, faulty equipment, and power lines, account for a significant portion of wildfires.
Different wildfire prevention strategies vary in effectiveness. Prescribed burns, for instance, can reduce fuel loads and create firebreaks, while improved building codes and defensible space around homes minimize property damage. Community education and public awareness campaigns are crucial for reducing human-caused ignitions.
- Implement stricter regulations on land development in high-risk areas.
- Increase funding for forest management and fuel reduction projects.
- Improve public education campaigns on wildfire safety and prevention.
- Invest in advanced wildfire detection and suppression technologies.
- Strengthen building codes and enforce defensible space requirements.
Consequences and Impacts of Climate Change-Fueled Wildfires, Climate change: What role is it playing in the California fires
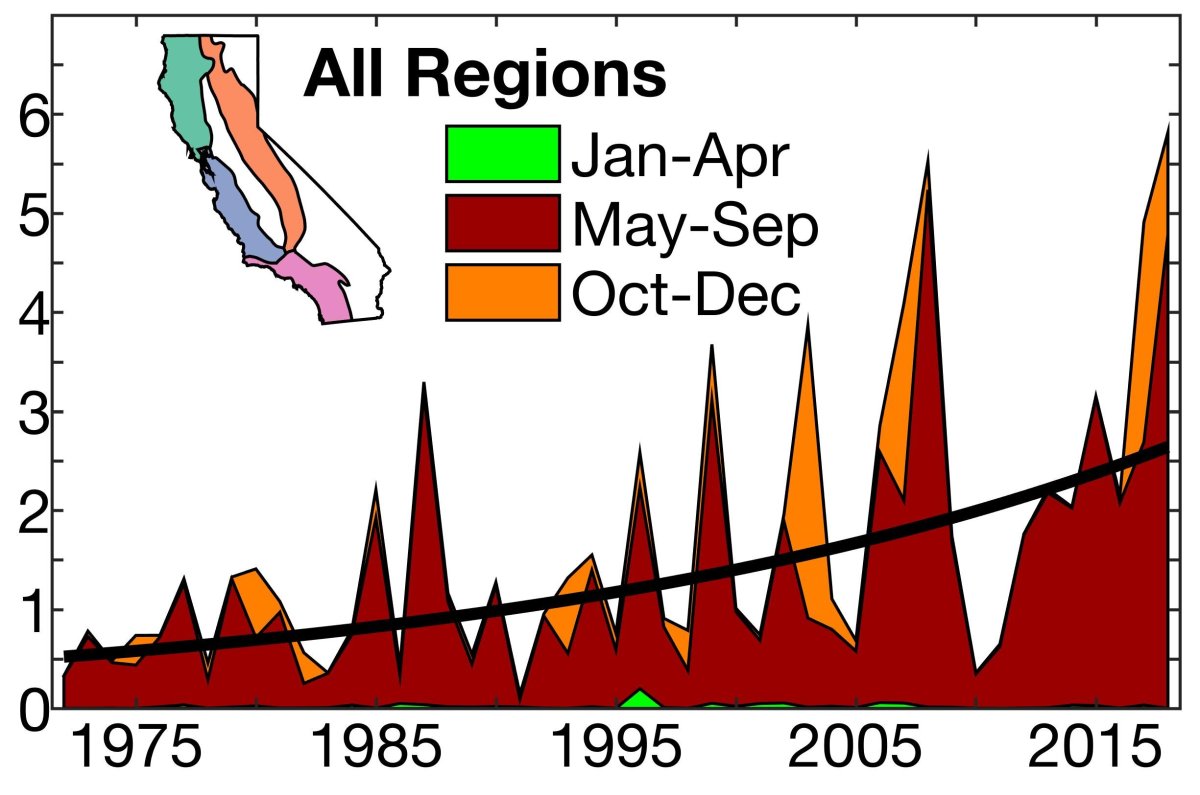
The consequences of climate change-fueled wildfires in California are far-reaching and devastating. The economic costs are immense, including property damage, firefighting expenses, and lost tourism revenue. Increased wildfire activity has severe environmental consequences, leading to habitat loss, soil erosion, and air pollution. Wildfire smoke poses significant health risks, causing respiratory illnesses and cardiovascular problems in affected populations.
Wildfires also have a significant impact on biodiversity and ecosystems, destroying habitats and threatening endangered species. The cascading effects extend to water resources and infrastructure, impacting water quality, reservoir levels, and the stability of critical infrastructure.
Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies
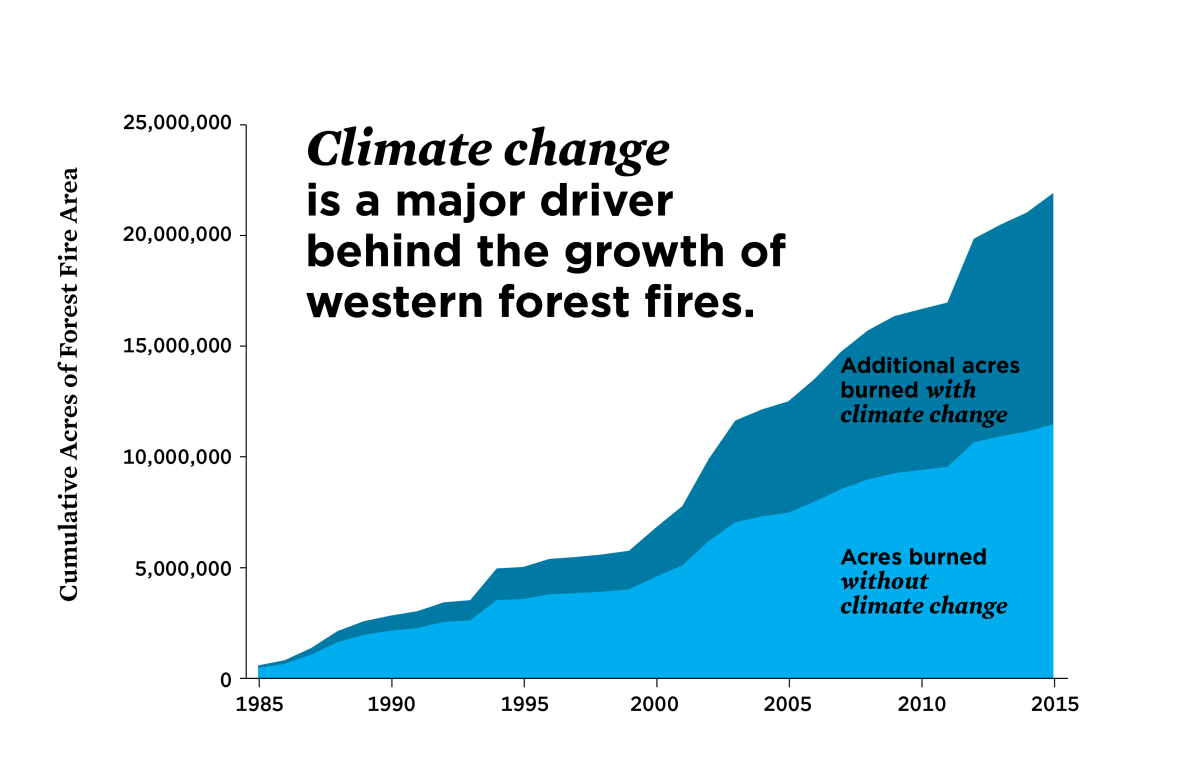
Mitigating climate change through greenhouse gas emission reductions is crucial for reducing the long-term risk of wildfires. Improving forest management practices, such as controlled burns and forest thinning, can significantly reduce fuel loads and make forests more resilient to fire. Community-level adaptation measures, including improved evacuation plans and community-based wildfire preparedness programs, can help reduce the impact of wildfires on communities.
California’s wildfires are getting worse, fueled by hotter, drier conditions linked to climate change. It’s a serious issue, and while you’re dealing with that, you might need a break – check out this hockey game recap: Dubois scores twice, lifts Capitals past Canucks in OT. After that exciting game, remember to think about how we can all contribute to mitigating the effects of climate change and reducing the risk of future devastating wildfires.
Different approaches to wildfire suppression and prevention exist, ranging from traditional methods like ground crews and air tankers to more advanced technologies like drones and remote sensing. A combination of strategies is often necessary to effectively manage wildfire risk.
California’s wildfires are getting worse, fueled by climate change’s impact on drought and extreme heat. It’s a serious issue, and sometimes you need a distraction, like checking out the awesome lineup for Bonnaroo 2029 – Megadeth, Queens of the Stone Age and More Set for Bonnaroo 2029 – before diving back into learning more about how climate change is affecting the state’s fire seasons.
Understanding these connections is key to finding solutions.
- Invest in renewable energy sources and improve energy efficiency.
- Implement stricter regulations on greenhouse gas emissions from vehicles and industries.
- Promote sustainable land use practices and protect natural habitats.
- Strengthen building codes and encourage fire-resistant construction materials.
- Develop and implement comprehensive wildfire preparedness plans at the community level.
Conclusive Thoughts
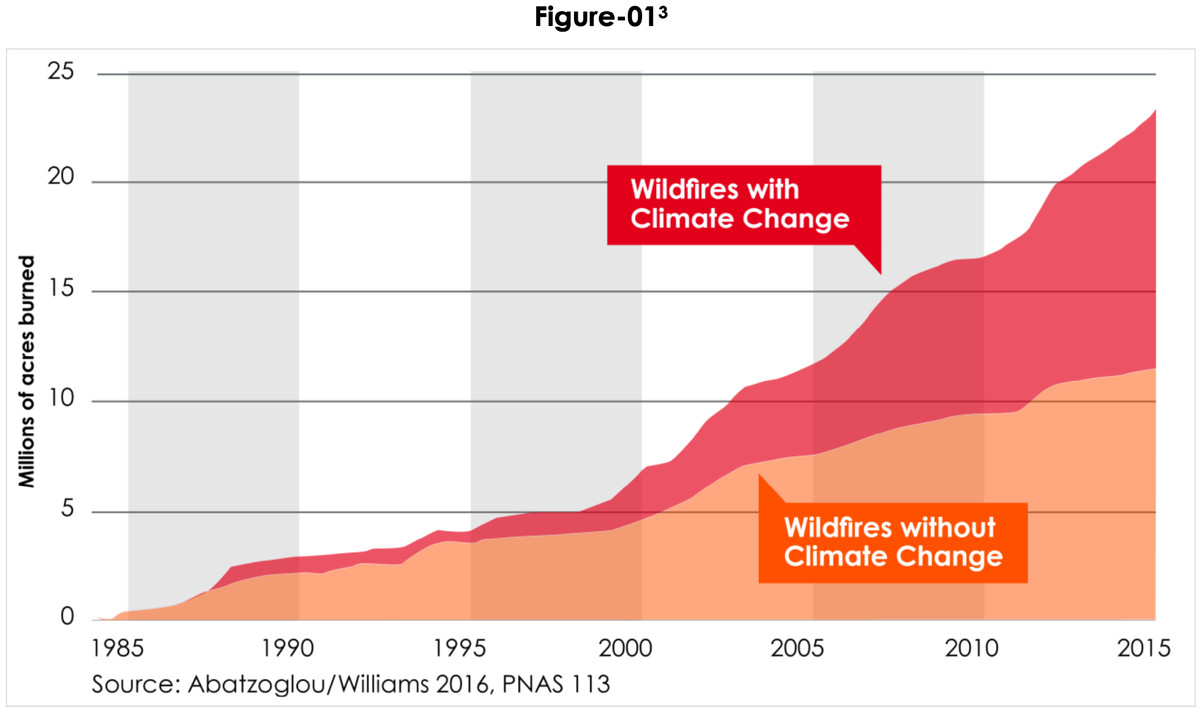
California’s wildfires are a stark illustration of climate change’s devastating power. Understanding the complex interplay between rising temperatures, drought, altered weather patterns, and human actions is crucial. While suppressing fires remains vital, the long-term solution lies in addressing the root cause: climate change. By reducing greenhouse gas emissions, implementing effective forest management practices, and fostering community resilience, we can work towards a future where devastating wildfires are less frequent and less intense.
The fight is far from over, but understanding the problem is the first step towards a solution.
Frequently Asked Questions: Climate Change: What Role Is It Playing In The California Fires
What specific vegetation changes contribute to increased wildfire risk?
Climate change is leading to the expansion of drier, more flammable vegetation types in California, replacing some moisture-retaining species. This creates more fuel for fires.
How does wildfire smoke affect human health?
Wildfire smoke contains harmful pollutants that can cause respiratory problems, cardiovascular issues, and eye irritation. Long-term exposure can have significant health consequences.
What role do insurance companies play in wildfire risk?
Insurance companies are increasingly factoring wildfire risk into premiums and coverage, leading to higher costs or even unavailability of insurance in high-risk areas.
Are there any legal implications related to wildfire damage and climate change?
There’s growing legal action against companies contributing to climate change, with some lawsuits focusing on the increased wildfire risk and associated damages.